What are Vibrating Wire Piezometers?
Vibrating Wire Piezometers (VWPs) are geotechnical instruments used to measure pressure changes within the ground. These changes are often attributed to changes in pore water pressure within soil, rock, or concrete. They are widely employed in various civil engineering and geotechnical applications to monitor groundwater levels, assess soil stability, and evaluate the integrity of structures such as dams, embankments, and tunnels.
The installation process of most Vibrating Wire Piezometers involves drilling boreholes to the required depth. Once the borehole is complete, VWPs are inserted into the hole at the required depth.
Sight Automation Solution
Sight Automation, the monitoring brand of ground investigation company Central Alliance, provide a complete in-house drilling, instrumentation and data hosting service for VWPs. Depending on specification, the team can instrument a borehole using single or multi-channel nodes to target specific depths of interest with a positional approach.
For Vibrating Wire Piezometers, Sight Automation can create alerts for changes in the ground at the passing of a certain defined threshold or when changes occur within a short time scale. This provides security for clients giving them confidence with data to make decisions. Utilising the flexibility of our flagship Sight Automation portal, we can design and create a personalised online data environment to to suit the specific requirements of your site.
Contact us to discuss how our instrumentation and hosting can revolutionise your data collection.
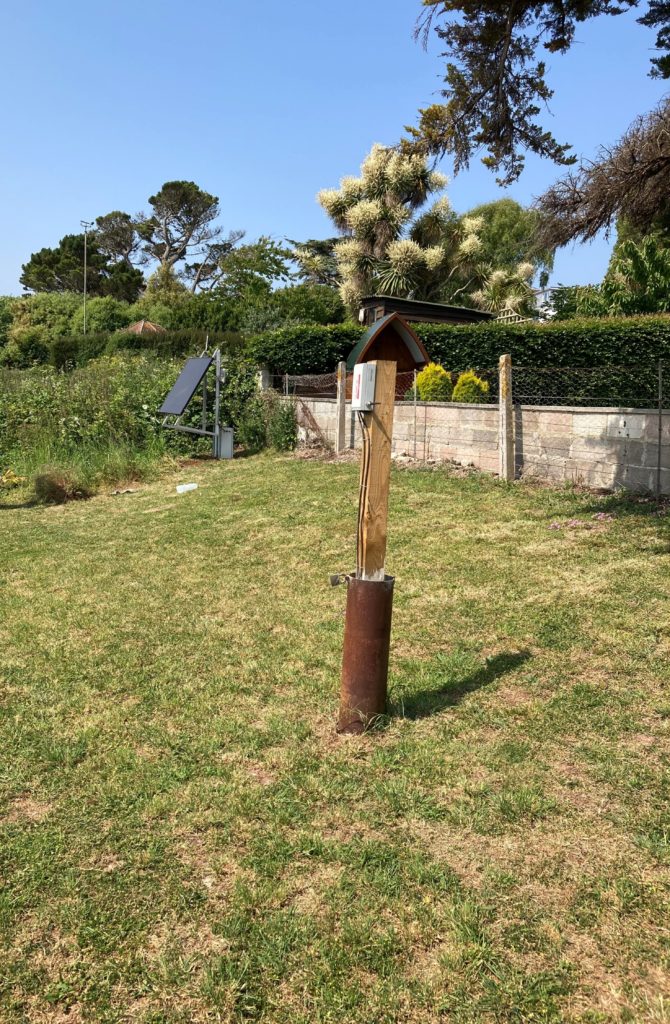

Image of Sight Automation gateway and VWP installation. The client specified a wooden post to be installed when instrumenting an existing historic borehole.
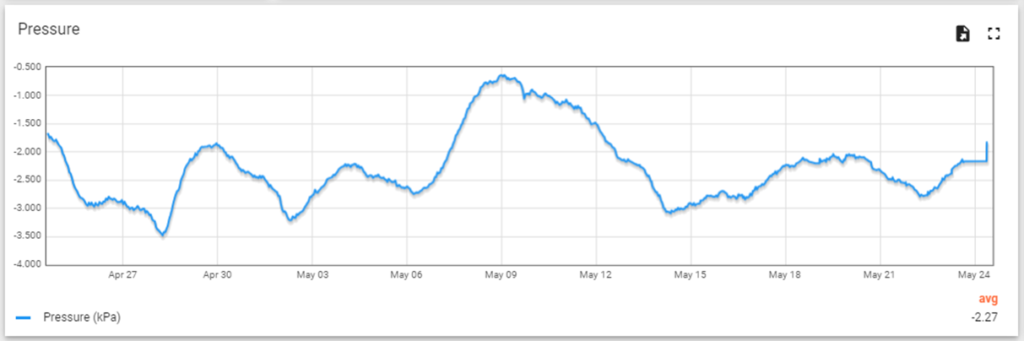
Sight Automation graph in the Portal showing a time plot to show ground pressure changes. This was used to interpret pore water pressure.
